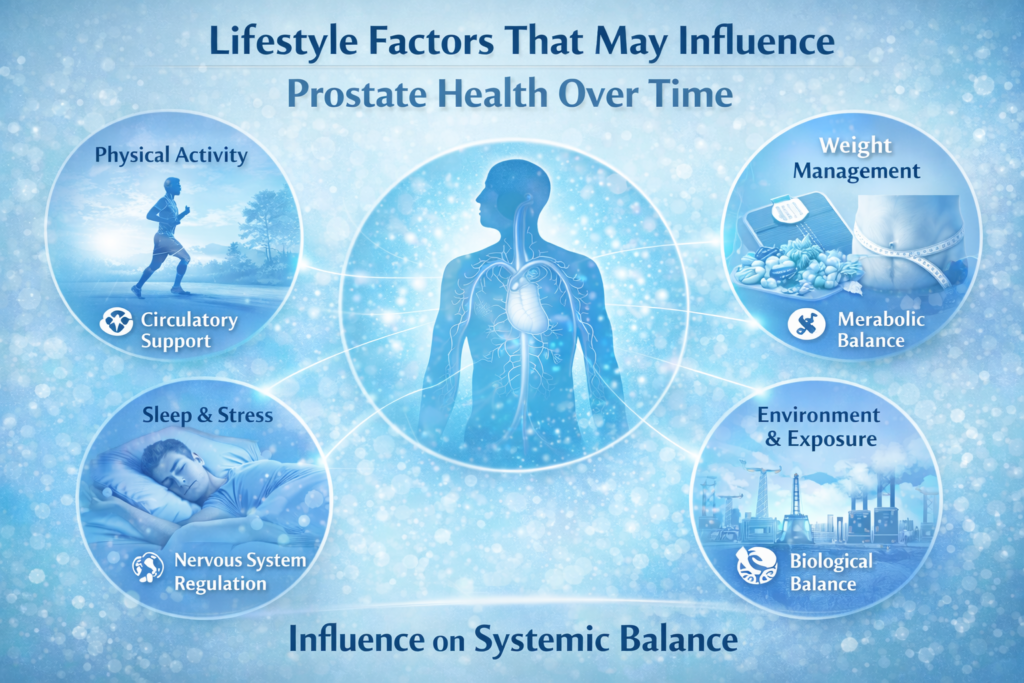
Prostate health is shaped by a complex interaction of biological processes that evolve over time. Alongside aging-related changes in inflammation, circulation, and oxidative balance, researchers increasingly examine how lifestyle patterns may influence prostate health as part of broader physiological regulation.
Rather than acting as direct causes, lifestyle factors are studied for their potential role in supporting overall systemic balance that may indirectly affect prostate function.
Lifestyle and Prostate Health: A Systems Perspective
From a research standpoint, the prostate does not function in isolation. It responds to hormonal signals, vascular conditions, immune activity, and metabolic regulation—all of which are influenced by daily habits.
This systems-based perspective helps explain why lifestyle factors are commonly studied alongside prostate health, particularly in aging populations.
Physical Activity and Circulatory Support
Regular physical movement is consistently associated with improved circulation and metabolic regulation. Research explores how movement patterns may support vascular responsiveness and inflammatory balance throughout the body.
While exercise is not framed as a treatment, maintaining physical activity is widely studied for its role in supporting long-term systemic health.
🎥 Video Overview: Lifestyle and Prostate Health
(A brief visual explanation exploring how daily habits are studied in relation to long-term prostate health.)
Nutrition Patterns and Metabolic Balance
Rather than focusing on individual foods, research increasingly examines dietary patterns. Balanced nutritional approaches are studied for their influence on metabolic health, oxidative processes, and inflammatory signaling.
These systemic effects may shape the internal environment in which prostate tissue adapts over time.
Weight Management and Hormonal Context
Body composition and metabolic status influence hormone signaling and inflammatory activity. Research suggests that maintaining metabolic balance may support broader physiological regulation, including systems connected to prostate function.
Importantly, studies emphasize gradual, sustainable patterns rather than short-term interventions.
Sleep, Stress, and Nervous System Regulation
Sleep quality and stress regulation play a role in hormonal rhythms and immune balance. Disrupted sleep or chronic stress can influence systemic signaling pathways that interact with inflammatory and metabolic processes.
Researchers increasingly explore how nervous system regulation contributes to long-term health outcomes across multiple organ systems.
Environmental and Behavioral Factors
Lifestyle research also considers environmental exposures and daily behaviors that may influence biological balance. These factors are studied in the context of cumulative effects rather than isolated causes.
The emphasis remains on overall patterns rather than individual habits viewed in isolation.
Interpreting Lifestyle Research Responsibly
🎥 Video Overview: Lifestyle and Prostate Health
(A brief visual explanation exploring how daily habits are studied in relation to long-term prostate health.)
Lifestyle-related findings are typically based on associations observed across populations. Individual responses vary widely, and no single lifestyle factor determines prostate outcomes.
Research highlights the importance of context, consistency, and long-term patterns rather than quick or isolated changes.
Final Thoughts
Lifestyle factors are increasingly recognized as part of the broader context in which prostate health evolves over time. Rather than acting as direct interventions, daily habits influence systemic processes—such as circulation, inflammation, and metabolic balance—that shape how prostate tissue adapts with age.
Viewing prostate health through a lifestyle lens supports a holistic understanding grounded in balance, consistency, and long-term physiological context.